SMS Marketing for eCommerce: How Top Brands Drive 5X ROI
Discover how top eCommerce brands use SMS marketing to drive 5X ROI. Learn proven strategies.

Learn about Ansoff’s Growth Model, its four strategies, and how it helps businesses plan for growth and market expansion.
In today’s competitive business landscape, companies must continuously evolve to stay relevant, increase their market share, and achieve sustainable growth. One of the most effective tools for driving business expansion is Ansoff’s Growth Model, also known as the Ansoff Matrix.
Created by Russian-American mathematician and business theorist Igor Ansoff, this model helps organizations identify and pursue various strategies for growth by examining markets and products.
Whether you’re running a startup or managing a well-established business, understanding the Ansoff Matrix can offer powerful insights into how you can expand your market presence and product offerings. Let’s dive into the core strategies of Ansoff’s Growth Model and explore how businesses can leverage it to achieve success.
Ansoff’s Growth Model revolves around four core strategies that provide a structured framework for business expansion. These strategies are based on the relationship between products and markets and the risks involved in each approach. The four strategies are:
Each of these strategies represents different ways a business can grow, and the key lies in determining which strategy aligns with your company’s goals, market conditions, and risk tolerance.
Market Penetration is the least risky of the four strategies. It involves selling more of your existing products to your current customers. This approach is often the first step for businesses seeking growth because it focuses on deepening market share in an already familiar environment.
Companies looking to increase their market share by using tactics like promotional campaigns, lowering prices, or enhancing distribution efforts to attract more customers within the same market. For example, a fast-food chain could launch a limited-time offer on its best-selling burger to entice repeat customers.
The main advantage of market penetration is the lower risk associated with working in familiar territory. The company already understands the customer base and the competitive landscape.
However, it does have limitations. There’s a ceiling to how much market share you can gain, especially if the market is already saturated.
Product Development involves creating new products to serve the existing market. This strategy is more aggressive than market penetration as it requires companies to innovate or refine their current offerings to meet the evolving needs of their customer base.
For instance, a smartphone manufacturer may release a new line of accessories, such as wireless chargers, to complement their current phones. This strategy allows businesses to diversify their offerings without stepping outside their established customer base.
Product development can breathe new life into a company’s product line and increase customer loyalty. By innovating, companies can stand out from competitors and potentially capture a larger market share.
There’s an inherent risk in developing new products, especially if they don’t resonate with the market or meet customer expectations. Investment in research and development can also be significant, but there’s no guarantee of success.
Market Development is the strategy of expanding into new markets with existing products. This approach is ideal for businesses looking to reach new customer segments, whether through geographic expansion or targeting new demographic groups.
A popular example would be a fashion retailer opening stores in a foreign country or launching an e-commerce platform to sell products internationally. Market development can also mean targeting different age groups or economic classes with the same product.
By entering new markets, companies can access untapped revenue streams and reduce their reliance on existing markets. This can be particularly beneficial if the current market becomes stagnant.
Entering a new market comes with its own set of challenges, including unfamiliar customer behavior, regulatory hurdles, and increased competition. It’s crucial to conduct thorough market research before diving into new territories.
Diversification is the most adventurous and risky strategy in the Ansoff Matrix, as it involves both new products and new markets. Companies that pursue diversification are entering entirely unfamiliar territory.
For instance, a software company might start offering hardware solutions such as laptops or computer accessories. Alternatively, a fashion brand may enter the food industry by opening restaurants.
The potential rewards of diversification are high. If successful, it opens up new revenue streams and can protect a company from market downturns in its original product category.
However, diversification also carries the highest level of risk since companies are stepping into uncharted waters. Without the proper research, businesses can face high costs and potential failure.
A key feature of the Ansoff Matrix is its ability to assess the level of risk associated with each strategy. As businesses move from market penetration to diversification, the risk increases due to a higher level of uncertainty and the resources required to succeed.
For example:
Understanding these risks allows businesses to make more informed decisions and choose the right growth strategy for their current position and long-term goals.
The Ansoff Matrix is not just a theoretical tool; it has practical implications for business strategy. Companies use it to plan their growth by evaluating their current market conditions, product offerings, and expansion opportunities.
Strategic planning using the Ansoff Matrix ensures that businesses align their growth efforts with their overall vision and resources. For example, a company might use market penetration to boost revenue in the short term while also developing new products to fuel long-term growth.
Let’s explore some real-world examples of how companies have successfully implemented each strategy:
Each of these examples demonstrates how businesses can use the Ansoff Matrix to tailor their growth strategy to their unique circumstances.
Applying the Ansoff Matrix is a step-by-step process that businesses can follow to identify the most suitable growth strategy. Start by assessing your current market position, resources, and long-term goals. Once you’ve chosen a strategy, develop a plan to implement it, making sure to monitor progress and adapt as necessary.
There are several key advantages to using the Ansoff Matrix for business growth:
While the Ansoff Matrix is a powerful tool, it has its limitations. One challenge is that it simplifies the complex nature of markets and product development. Businesses operating in dynamic, fast-changing industries may need to complement the Ansoff Matrix with other tools such as SWOT analysis or Porter’s Five Forces.
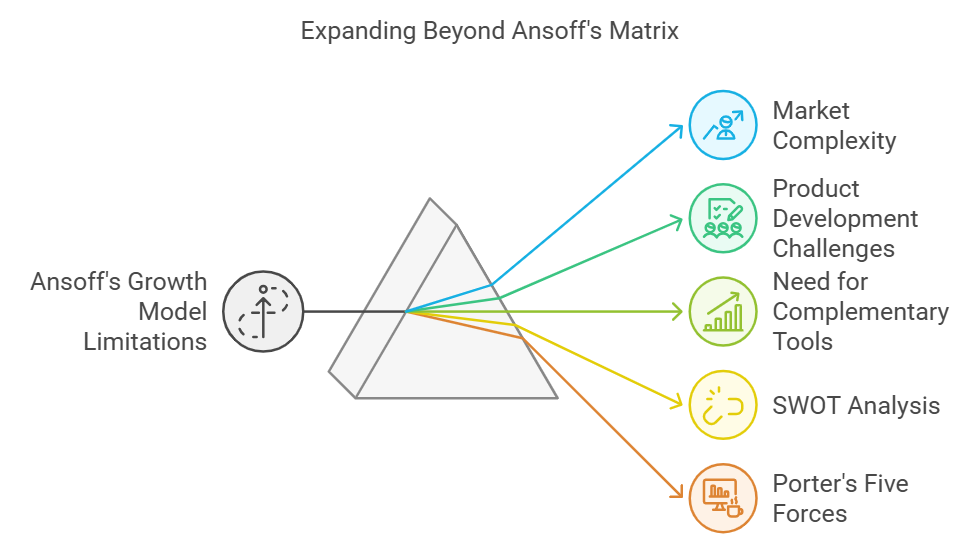
Combining the Ansoff Matrix with other business analysis tools enhances its effectiveness. For example, a SWOT analysis can help businesses evaluate internal strengths and weaknesses, while Porter’s Five Forces examines external competitive pressures.
When implementing Ansoff’s strategies, businesses should:
In conclusion, the Ansoff Growth Model offers a powerful framework for businesses seeking to expand their market presence and product offerings. By understanding the risks and rewards of each strategy, companies can make informed decisions that align with their growth goals.
Whether you’re aiming for market penetration or contemplating diversification, the Ansoff Matrix provides the structure and insights needed to achieve sustainable growth.